Rotational Molding is a very versatile process of creating virtually all kinds of mostly hollow Plastic Parts. The phrase is often shortened to the word rotomolding.
Process of Rotational molding
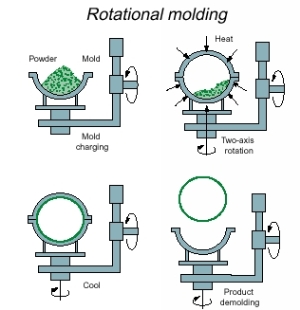
The rotational molding process is a high temperature, low pressure plastic forming process that uses heat and biaxial rotation (i.e. rotation on two axes) to produce hollow, one piece parts.
Critics of the process point to it's long cycle times- only one or two cycles an hour can typically occur, as opposed to other processes such asinjection molding, where parts can be made in a few seconds. The process does have distinct advantages though. The manufacture of large, hollow parts such as oil tanks is much easier by rotational molding than any other method. Rotational molds are significantly cheaper than other types of mold too- in the order of hundreds of US Dollars, rather than thousands as for other polymer processing molds.
The rotational molding process consists of four distinct phases:
1- Loading a measured quantity of polymer (usually in powder form) into the mold.
'2- Heating the mold in an oven whilst it rotates, until all the polymer has melted and adhered to the mold wall. The length of time the mold spends in the oven is critical- too long, and the polymer will degrade, reducing impact strength. If the mold spends too little time in the oven, melting of the polymer may be incomplete. The polymer grains will not have time to fully melt and coalesce on the mold wall, resulting in large bubbles in the polymer. This has an adverse effect on the mechanical properties of the finished product.
3- Cooling of the mold, usually by fan. This stage of the cycle can be quite lengthy too- the polymer must be cooled to a temperature where it solidifies and can be handled safely by the operator. This typically takes tens of minutes. The part will shrink on cooling, coming away from the mold, and facilitating easy removal of the part. The cooling rate must be kept within a certain range- very rapid cooling (e.g., by water spray) would result in the part cooling and shrinking at an uncontrolled rate, producing a warped part.
4- Removal of the part.
Recent Improvements in Rotational Molding
Until recently the process was largely empirical, relying on both trial and error and the experience of the operator to judge when the part should be removed from the oven, and when it was cool enough to be removed from the mold. However technology has improved in recent years which allows the internal air temperature in the mold to be monitored, removing much of the guesswork from the process.
Much of the current research is looking into lowering the long cycle times as well as improving part quality. The most promising area is within mold pressurisation- it is well known that applying a small amount of pressure internally to the mold at the correct point in the heating phase of the cycle speeds up the coalescence of the polymer particles during the melting phase, producing a part with less bubbles in a shorter period of time than at atmospheric pressure. This pressure also delays the separation of the part from the mold wall due to shrinkage during the cooling phase, aiding removal of heat from the part and therefore speeding the cooling phase too. The main drawback to this is the danger of explosion of a pressurised part to the operator- something that has prevented mold pressurisation becoming adopted on a large scale by rotomolding manufacturers.
Materials
More than 80% of all the material used in Rotomolding is polyethylene. Other artificial compounds are PVC plastisols, Nylons, polypropylene.
Natural Materials: Its only been possible relatively recently, but natural materials can also be used. Through the use of real sands and stone chip, sandstone composite can be created which is 80% natural non-processed material.
Product Design
Rotationally molded parts have to follow some restrictions that are somewhat different from other plastic processes. Being a low pressure process, sometimes designers face hard to reach areas in the mold. Good quality powder may help to overcome some situations, but usually the designers have to keep in mind that it's not possible to make some sharp threads used in injection molded goods. Some products based on polyethylene can be put in the mold before filling it with the main material. This can help to avoid holes that otherwise would appear in some areas. This could be also achieved using molds with movable sections.
Molds
Mold are typically fabricated from either mild steel and stainless steel sheets or aluminum casted. Aluminum molds are usually many times thicker than an equivalent steel molds, as it is a much less hard metal. This thickness doesn't affect cycle times significantly because aluminum's thermal conductivity is many times greater than that of steel. Aluminum molds tend to be more expensive than similar steel molds.

This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteHi Guy's,
ReplyDeleteWe are responsible for our environment. More than 80% of all the material used in Rotomolding is polyethylene. Other artificial compounds are PVC plastisols, Nylons, polypropylene so reuse it.for more info visit:- http://www.rotovacgroup.ca/
The procedure is also labour-intensive, and it can be hard to locate excellent workers. These processes are frequently used to manufacture bottles for beverages like water and juice. Extrusion processes are utilized to earn pipe, sheeting, films, and assorted forms. Source for more about Roto-molding.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteIt is advised that you let the mold testing companies know that you are paying for it and inform them of the type of mold you think you might have in your building.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteWith the use of the latest technology and a strong understanding of how each of these components work together, they can create custom designs for your product in any color, size, or shape you need. For more information on granger plastics company, read me.
ReplyDeleteRotational molding typically involves a hot metal mold that is punctured with an injection charge or Shot glass, which is then filled with plastic. Get more Interesting details about rotomolding on rotational molding.
ReplyDeleteThen, the part is rotated on a second set of axes. The process continues until the plastic has hardened.The next step in rotational molding is the reduction of the solid polymer to a powder form. If you want to know more about rotomolding, you can find its details on grangerplastics.com.
ReplyDeleteThe goal is to maximize the efficiency of the machine and create a high-quality end product. Custom Roto-molding is also a popular manufacturing method for creating a variety of trinkets and toys.
ReplyDeleteI just need to say this is a well-informed article which you have shared here about hoodies. It is an engaging and gainful article for us. Continue imparting this sort of info, Thanks to you. lztooling.com
ReplyDelete